When you hear the word “ester,” it’s almost like a little bell goes off, isn't it? You might be thinking of a person, perhaps someone well-known, or maybe even something entirely different. The truth is, that word, “ester,” has a few interesting paths it can take, depending on where you’re looking. It’s a word that, in some respects, pops up in a couple of very distinct areas, and it’s pretty fascinating to see how they connect, or rather, how they don’t, in a way.
Actually, if you’re thinking about the world of chemistry, an ester is a particular kind of compound. It's essentially something that comes from an acid, whether that acid is organic or inorganic, where a hydrogen atom from a certain part of that acid, specifically from what’s called an acidic hydroxyl group, gets swapped out. So, it's replaced by something else, which makes it a new sort of molecule entirely, which is kind of neat, you know?
Then, on the other hand, you have "Esther," spelled with an 'h' usually, who is a really important figure from an old story. She's the main character, the heroine if you will, of a book found in the Hebrew Bible. She was, apparently, the wife of a Persian king, King Ahasuerus. It’s quite a different kind of "ester" altogether, isn't it? So, you see, the word itself can lead you down very different roads.
- Carl Bismarck Meme
- Pov Mom And Son
- Jacob Savage Just For Gays
- Dti Embraced By Lace
- Hong Kong Tijuana Meme
Table of Contents
- What's in a Name - Exploring the Idea of Ester
- What is an Ester in Chemistry, anyway?
- How do we even get these Ester Compounds?
- Who was Esther, and why does that name come up?
- Are there different kinds of Esters, chemically speaking?
- What are some everyday uses for Esters?
- Naming Esters - A Little Bit About How It Works
What's in a Name - Exploring the Idea of Ester
It’s really something how a single word can bring up such different thoughts, isn't it? When someone says "ester," your mind might jump to a person you know, or maybe a public figure. But then, if you look at it from a scientific angle, it means something else entirely. This kind of double meaning, or rather, having a word that sounds similar but points to very different things, is pretty common in language. It makes you think about how we use words and what we expect them to mean, you know? So, depending on your background or what you are looking for, the word "ester" can mean a chemical compound, or it could be the name of a person from an ancient text. It’s actually quite a cool linguistic quirk, if you think about it.
So, we're going to talk about both of these ideas, the chemical one and the historical one. We won't be guessing about what you might have been looking for, but rather giving you some clear details about what these "esters" are, based on information that's pretty well-established. This way, whether you're interested in science or old stories, you'll get a better idea of what this word can mean. It's about exploring the different facets of a word that, apparently, has more than one important meaning.
What is an Ester in Chemistry, anyway?
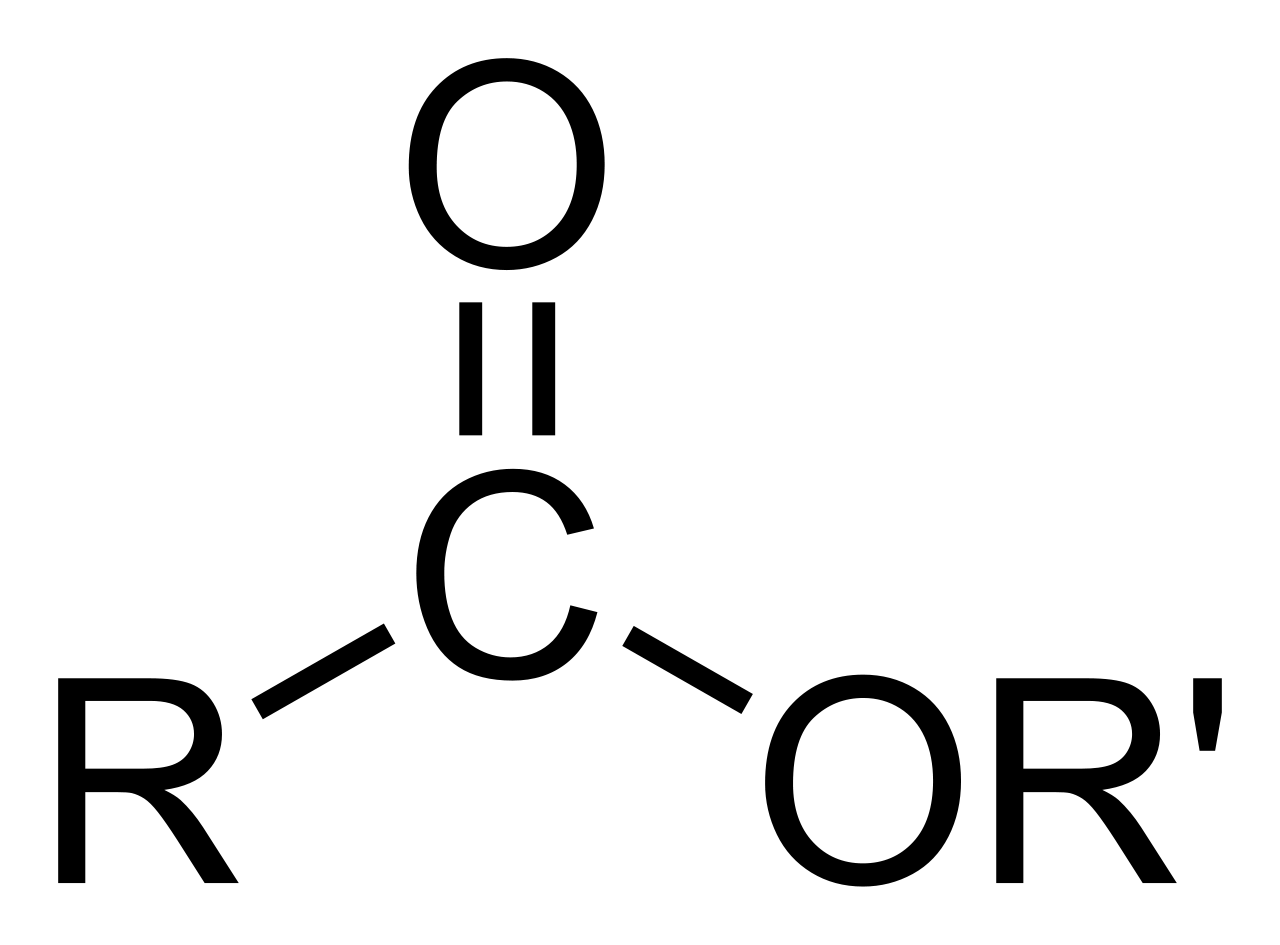
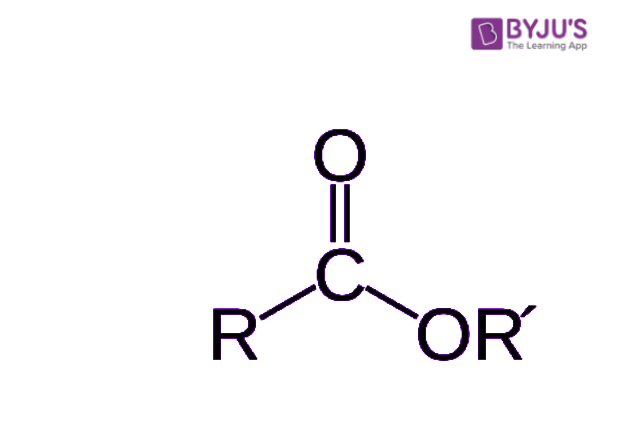
Okay, let's get into the chemistry side of things first. When we talk about an ester in this context, we're talking about a chemical compound. It's kind of interesting how these things are put together. An ester comes from an acid, and that acid can be either organic, meaning it has carbon in its structure, or inorganic, which would be an acid without carbon. The key thing that makes it an ester is a specific change that happens to the acid. You see, the hydrogen atom, which is usually found in at least one of the acid's hydroxyl groups – that's a part of the molecule made of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom joined together – gets swapped out. It gets replaced by something else, usually a hydrocarbon group, which is basically a chain of carbon and hydrogen atoms. This replacement is what turns the acid into an ester. It's a pretty neat trick that molecules perform, really.
- Me Ofendiste Shrek
- Get A Job N
- Sean Omalley Vs Merab Highlights
- Just Gimme My Money Kai Cenat
- Smokey Robinson Dancing
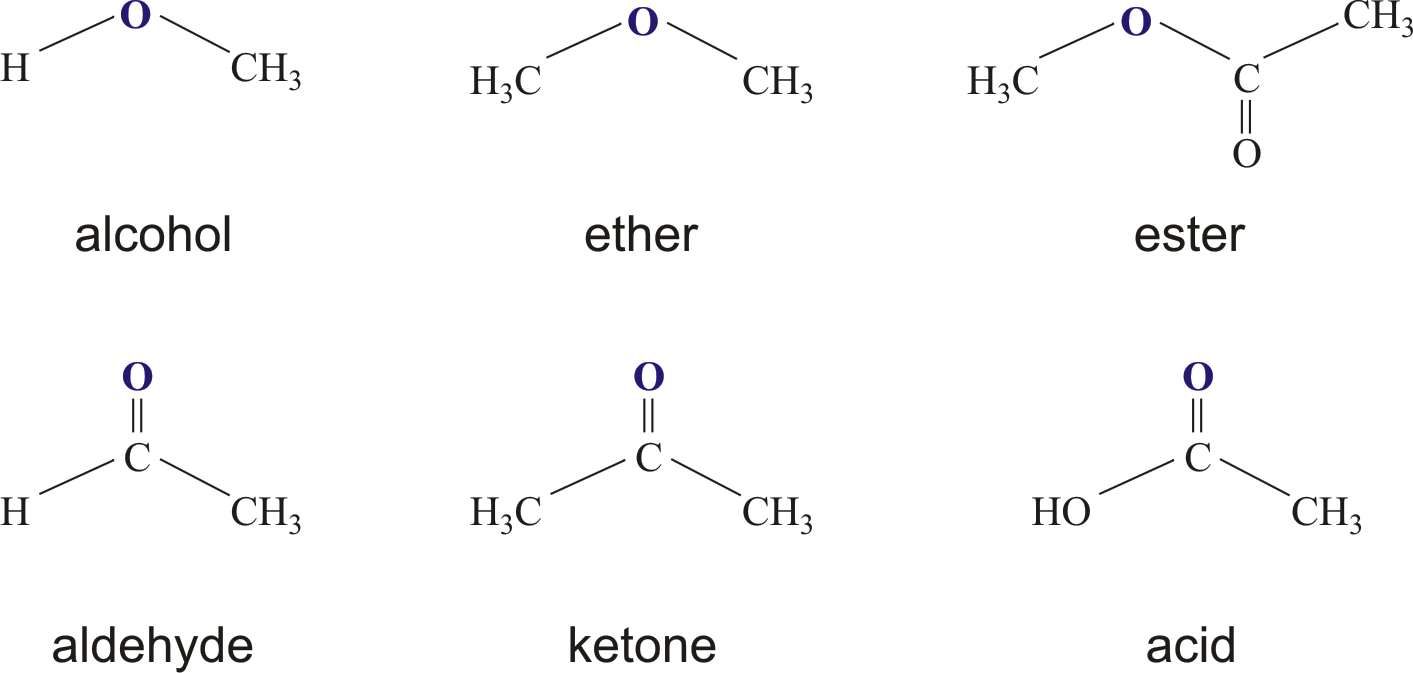
These compounds are a big group of organic chemicals, and they have a particular way of reacting with water. When an ester mixes with water, it can actually break down and give you back an alcohol and either an organic acid or an inorganic acid, depending on what it was made from in the first place. It’s like a reverse process, in a way, of how they were created. The most common types of esters, the ones you hear about most often, are the ones that come from carboxylic acids. These are a very important kind of organic acid, and their esters show up all over the place, as we'll see later on. They have a particular structure that makes them behave in certain ways, and that's what makes them so useful, too.
The Basic Makeup of an Ester Exposito Erome Connection
So, what does an ester actually look like on a molecular level? Well, if you could peek inside, you’d see that an ester is an organic compound where a hydrogen atom that was part of the compound's carboxyl group – that's a specific arrangement of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms – has been taken out. In its place, a hydrocarbon group has been put in. This is what really sets an ester apart from its parent acid. These esters, as we mentioned, come from carboxylic acids, and they have a distinct kind of structure. You'll often see them with a carbon atom double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to another oxygen atom, which then connects to another carbon atom. This second oxygen atom, the one that's single-bonded, is actually connected to another carbon atom, which forms the hydrocarbon part that replaced the hydrogen. It's a key part of their structure, this particular arrangement of atoms, and it’s what gives them their special qualities, you know?
There's also an interesting bit of history with some of these compounds. For example, a common compound that is technically a type of ester, though it might not always be called that in everyday talk, is glyceryl. While its proper chemical name might be something more involved, almost everyone just calls it by its older, simpler name. This shows how sometimes, in the world of chemistry, old names stick around even when the technical terms get more precise. It's just a little detail that adds to the story of these compounds, isn't it?
How do we even get these Ester Compounds?
Creating an ester, chemically speaking, usually involves a process called esterification. It's pretty much what it sounds like – making an ester. This typically happens when you bring together an acid, like a carboxylic acid, and an alcohol. When these two kinds of molecules meet under the right conditions, they react. During this reaction, a water molecule is actually formed and then leaves the scene. This loss of water is a big part of what makes the ester form. It's a kind of condensation reaction, where two smaller molecules join up to make a larger one, and a small molecule like water is released. So, you're essentially taking bits from an acid and bits from an alcohol, putting them together, and out pops an ester and some water. It’s a pretty common way to make these compounds in a lab, or even in nature, apparently.
The core idea is that the hydrogen atom from the acid's hydroxyl group is replaced. So, if you have an acid with its characteristic -OH group, that hydrogen (H) atom gets swapped out for a hydrocarbon group that comes from the alcohol. It's a fundamental step in how these compounds are put together. This process is how many of the esters we encounter in our daily lives are made, whether they are produced industrially for specific purposes or occur naturally in plants and fruits. It’s a very versatile reaction, and it allows for the creation of a huge variety of different ester compounds, each with its own particular properties. It’s a basic building block, in a way, for a lot of organic chemistry.
Crafting Ester Exposito Erome Molecules
When you think about how these molecules are crafted, it’s all about swapping out one atom for a whole group of atoms. The acid starts with its characteristic part, and then an alcohol comes along, and they basically do a little molecular dance where a hydrogen from the acid and a hydroxyl from the alcohol join up to become water, leaving the rest of the acid and alcohol parts to connect. This new connection forms the ester bond. This bond is what gives esters their unique properties, like their smells or how they dissolve in different things. It’s pretty cool how specific these molecular arrangements are, and how they dictate what the compound can do. You can think of it as a chemical building block, where different pieces fit together in a very particular way to create a new kind of structure, a sort of molecular architecture, if you will. The precise arrangement of atoms in an ester, especially that second oxygen atom bonding to another carbon, is what makes it an ester and not something else. It's a very specific kind of chemical signature.
Who was Esther, and why does that name come up?
Now, let's shift gears completely and talk about "Esther," spelled with an 'h.' This is a very different kind of "ester" altogether. Esther, also known by her original name Hadassah bat Avihail, is a truly significant figure in an old, old story. She is the main character, the namesake, of the Book of Esther, which is a part of the Hebrew Bible. Her story is one of bravery and standing up for her people in a time of great danger. She lived in ancient Persia and became the wife of King Ahasuerus, who is often identified by historians with Xerxes I. Her journey from an ordinary young woman to queen is quite remarkable, and her story is celebrated every year during the Jewish holiday of Purim. It’s a tale that has been told for thousands of years, inspiring many with its message of courage and cleverness. So, when you hear "Esther," this is typically the person that comes to mind for many, and it's quite a powerful story, too.
Her story is full of twists and turns, involving palace intrigue, a wicked advisor, and a plan to harm her people. Esther, with the guidance of her cousin Mordecai, finds the strength to use her position as queen to intervene and save her community. It’s a narrative that explores themes of identity, faith, and standing up for what is right, even when it’s incredibly difficult. The Book of Esther is unique in the Bible in some ways, and it remains a beloved and often retold story. It's pretty amazing how a name can carry so much history and meaning, isn't it? This "Esther" has certainly left an indelible mark on culture and history, and her name is still very much in use today, which is kind of neat.
The Story of Esther and the Ester Exposito Erome Link
The connection between the name Esther and the broader "ester exposito erome" idea is, really, mostly about the sound of the word. People might hear "ester" and think of the name, which then brings to mind the historical figure. Her story is a testament to the idea that even in seemingly impossible situations, one person can make a tremendous difference. The narrative shows how she, a young woman, was able to influence a powerful king and overturn a decree that would have had terrible consequences. It’s a very human story, full of emotion and high stakes. The persistence and cleverness she showed are often highlighted when her story is discussed. So, while she isn't a chemical compound, her name shares a sound with one, and both have their own very distinct and important places in our collective knowledge, which is quite interesting, you know?
Are there different kinds of Esters, chemically speaking?
Yes, there are definitely different kinds of esters in chemistry. As we touched on, the ones derived from carboxylic acids are the most common and widely discussed. These are often called carboxylic esters. But the general idea of an ester is broad – it's any compound that comes from an acid where a hydrogen from a hydroxyl group is replaced. So, while carboxylic esters are a huge family, there are also esters of inorganic acids, like phosphate esters or sulfate esters, though these might be less familiar in everyday conversation. The key is that characteristic chemical bond and structure. It’s like a big family of molecules, and each member has its own little quirks and uses. The way they are made, through that reaction between an acid and an alcohol, is a pretty general method that can be applied to many different starting materials, giving rise to a wide array of ester compounds. This versatility is one of the reasons they are so important in chemistry and in many industries, actually.
Discovering what esters are really about involves looking at their structure and how they are formed. You learn about their rule for naming them and their possible uses, which gives you a good sense of their importance. Esters are organic compounds that come from carboxylic acids, and they have a carbon radical – that’s a part of a molecule with a carbon atom that has a free bond – in the place where the hydrogen atoms would usually be. This is what makes them different from the acids they come from. This little change in structure makes a big difference in how they behave and what they can be used for. It’s a subtle but powerful modification, really, that opens up a whole new set of chemical possibilities. So, yes, there are many varieties, and they are all quite fascinating in their own way.
Varieties of Ester Exposito Erome Compounds
The different classifications of esters really depend on what kind of acid they are made from, and what alcohol is used in their creation. For instance, if you use a short-chain alcohol and a short-chain acid, you might get an ester that smells like fruit. If you use longer chains, you might get something that feels more like a wax or a fat. The possibilities are, in some respects, almost endless when you consider all the different combinations of acids and alcohols that can react to form esters. Each combination creates a unique compound with its own specific properties, whether that's its boiling point, its smell, or how it reacts with other chemicals. It’s a pretty rich area of study in organic chemistry, and there’s still a lot to learn about all the different kinds of esters that exist in nature and those that can be made in a lab. The way they are obtained, through that esterification reaction, is a common thread that ties them all together, but their individual characteristics can vary quite a bit, you know?
What are some everyday uses for Esters?
Esters are actually all around us, even if we don't always realize it. They are very often responsible for the pleasant smells and flavors of many fruits and flowers. For example, that lovely smell of pineapple? That's thanks to an ester called methyl butanoate. And if you've ever smelled banana or pear, you've probably encountered isopentyl acetate, another ester. So, they play a big role in the natural world, giving things their characteristic aromas and tastes. This makes them really important in the food and fragrance industries. They are used to create artificial flavors and scents for everything from candies and drinks to perfumes and soaps. It’s pretty cool how these tiny molecules can have such a big impact on our senses, isn't it? They are also used as solvents in many industrial processes, helping to dissolve other substances. So, they are quite versatile, and you encounter them more often than you might think.
Beyond just smells and flavors, esters also show up in other places. Fats and oils, for instance, are actually a type of ester. They are formed from glycerol, which is an alcohol, and fatty acids. So, the cooking oil you use, or the fats in your food, are all examples of esters. They are also used in the production of plastics, such as polyesters, which are used to make fibers for clothing and bottles. So, from the scent of a fresh fruit to the clothes on your back, esters are pretty much everywhere. Their
Detail Author:
- Name : Bernardo Halvorson
- Username : eichmann.jaeden
- Email : vdouglas@damore.com
- Birthdate : 2006-03-15
- Address : 204 Dianna Hills Suite 937 Gerholdshire, GA 33205-7595
- Phone : 1-325-363-4680
- Company : Wolff-Toy
- Job : Armored Assault Vehicle Officer
- Bio : Rerum totam non cum et vel unde quis. Ea optio aspernatur non quo. Quasi rerum qui voluptas voluptatem harum. Mollitia dolor magnam alias excepturi repellendus molestiae laboriosam optio.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/lacey_lindgren
- username : lacey_lindgren
- bio : Ullam itaque eaque dolorem rerum et voluptas. Nemo sed consequuntur soluta quia est.
- followers : 5691
- following : 681
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/lacey.lindgren
- username : lacey.lindgren
- bio : Est quas ut quidem rerum odio aut. Aspernatur non est rem culpa nobis.
- followers : 4013
- following : 2769
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/lindgren1984
- username : lindgren1984
- bio : Et est et delectus autem saepe et ut a.
- followers : 3782
- following : 1318
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/lindgren1995
- username : lindgren1995
- bio : Cum facilis est repellendus est quibusdam. Fuga ut laudantium doloribus qui esse voluptas odit. Nobis amet cupiditate quod expedita vero repellat id.
- followers : 4836
- following : 934